Welcome to WordPress. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start writing!
Category: Uncategorized
-
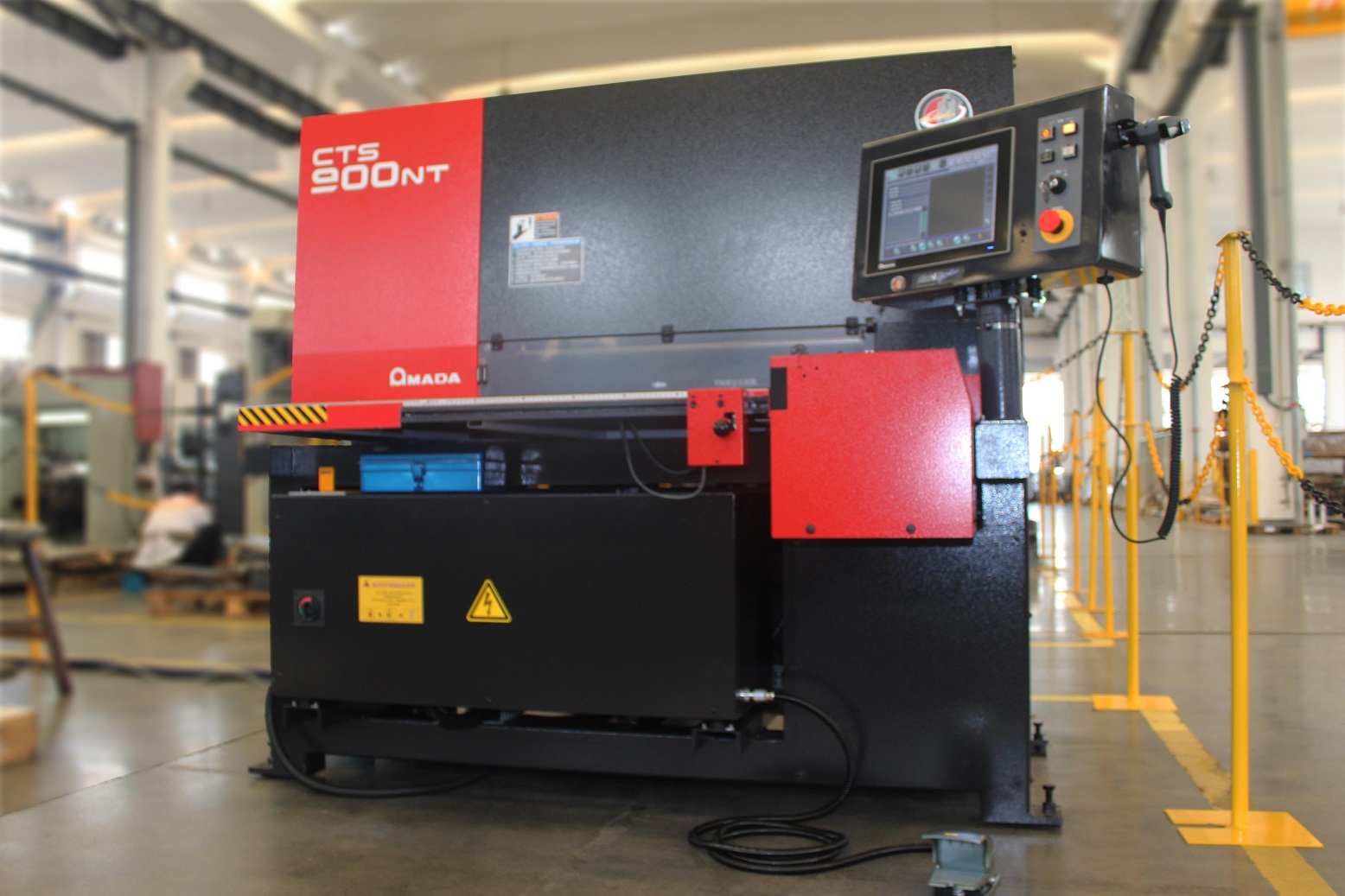

CNC Tapping Sheet Metal
In the world of modern manufacturing, precision and efficiency are paramount. CNC tapping, a highly automated machining process, plays a crucial role in achieving these goals. It offers a reliable and repeatable method for creating internal threads in metal parts, essential for countless applications across various industries
What is CNC Tapping Metal?
CNC tapping metal is a process that involves creating threads in metal using a computer numerical control (CNC) machine. The process involves using a tapping tool to create the threads, which are then used to attach other components or materials to the metal. CNC tapping metal is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
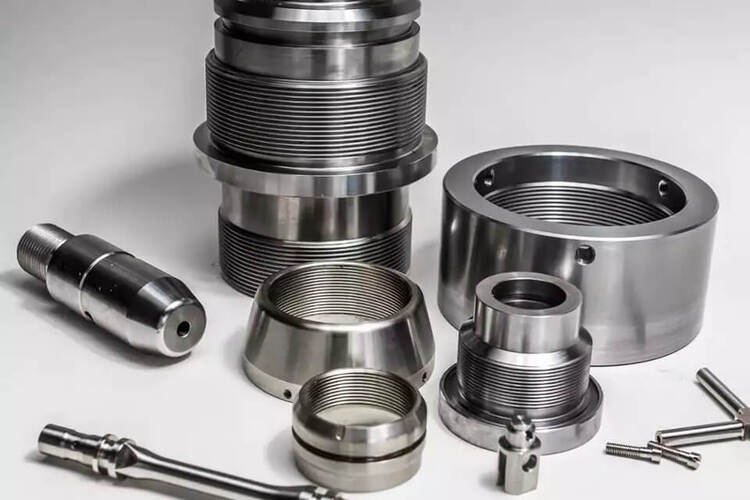

CNC Tapping Metal The CNC Tapping Process
CNC tapping utilizes a CNC machine to precisely control the rotation and depth of a cutting tool called a tap. This automated process ensures high accuracy and consistency, eliminating the variability associated with manual tapping. Here’s a breakdown of the process
Tool Selection
The choice of tap depends on the material being tapped, the thread size, and the desired thread quality. Common tap types include spiral points, spiral flutes, and form taps. Materials range from high-speed steel (HSS) for general-purpose applications to carbide for more demanding materials.
Machine Setup and Programming
The CNC machine’s spindle has a special holder for the tap. A program in G-code, which is a standard language for CNC machines, controls the tapping process. This program tells the tap how to move, how fast to spin, and how deep to go.
Cutting Parameters
Precise control over cutting parameters is critical for successful CNC tapping. These parameters include:
- Speed: The rotational speed of the tap, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
- Feed: The rate at which the tap advances into the workpiece, synchronized with the RPM to maintain the correct thread pitch.
- Depth: The final depth of the tapped hole.
Coolant and Lubrication
Proper coolant and lubrication are essential for extending tool life, improving thread quality, and preventing chip buildup. The specific coolant used depends on the material being tapped
Material Recommended Tap Type Cutting Speed (RPM) Aluminum Spiral Point 800-1500 Mild Steel Spiral Flute 400-800 Stainless Steel Spiral Flute (Coated) 200-400 Advantages of CNC Tapping Metal
CNC tapping offers numerous advantages over manual tapping, making it the preferred method for high-volume production and demanding applications:
- High Accuracy and Repeatability: CNC control ensures consistent thread depth and pitch, resulting in highly accurate and repeatable threads.
- Reduced Operator Fatigue: Automation minimizes operator involvement, reducing fatigue and the risk of human error.
- Improved efficiency and productivity: CNC tapping metal is a high-speed process, allowing for rapid production of threaded components.
- Consistent quality: CNC tapping produces very consistent, high-quality internal threads with tight tolerances. This means your parts will have a better fit and function, and less risk of thread failure or missing.
Types of Tapping Operations
There are several types of tapping operations, each with its unique characteristics and applications. The most common types of tapping operations include:
Type of Tapping Description Application Cut Tapping Involves cutting the threads into the metal using a tapping tool Suitable for most materials, including steel, aluminum, and copper Form Tapping Involves forming the threads into the metal using a tapping tool Suitable for materials with high tensile strength, such as stainless steel and titanium Thread Milling Involves using a milling tool to create the threads Suitable for large diameter threads and materials with high hardness Tools and Techniques
CNC tapping tools are designed to withstand the rigors of high-speed tapping operations. The most common types of CNC tapping tools include:
- Tapping bits: These are the cutting tools used to create the threads.
- Tapping holders: These are used to hold the tapping bits in place during the tapping operation.
- Collets: These are used to hold the tapping holders in place during the tapping operation.
To achieve optimal results, it is essential to use the right CNC tapping techniques. These include:
- Speed and feed rates: The speed and feed rates must be carefully controlled to avoid tool breakage and ensure accurate thread creation.
- Coolant systems: Coolant systems are used to keep the tapping tool and material cool during the tapping operation, reducing the risk of tool breakage and material deformation.
Applications of CNC Tapping Metal
CNC tapping finds applications in a wide range of industries, including:
- Aerospace: CNC tapping metal is used to create threaded components for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Automotive: CNC tapping metal is used to create threaded components for vehicles, including engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission components.
- Medical devices: CNC tapping metal is used to create threaded components for medical devices, including implants, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment.

Applications of CNC Tapping Metal CNC Tapping vs. Manual Tapping
Feature CNC Tapping Manual Tapping Speed High Low Accuracy High Moderate Repeatability Excellent Limited Cost Higher initial investment, lower per-part cost Lower initial investment, higher per-part cost Production Volume High Low to medium Conclusion
CNC tapping metal is a precise process that offers numerous benefits, including increased accuracy and precision, improved efficiency and productivity, and reduced material waste. By understanding the different types of tapping operations, CNC tapping tools and techniques, and common challenges and solutions, manufacturers can optimize their CNC tapping metal processes and achieve optimal results.
-
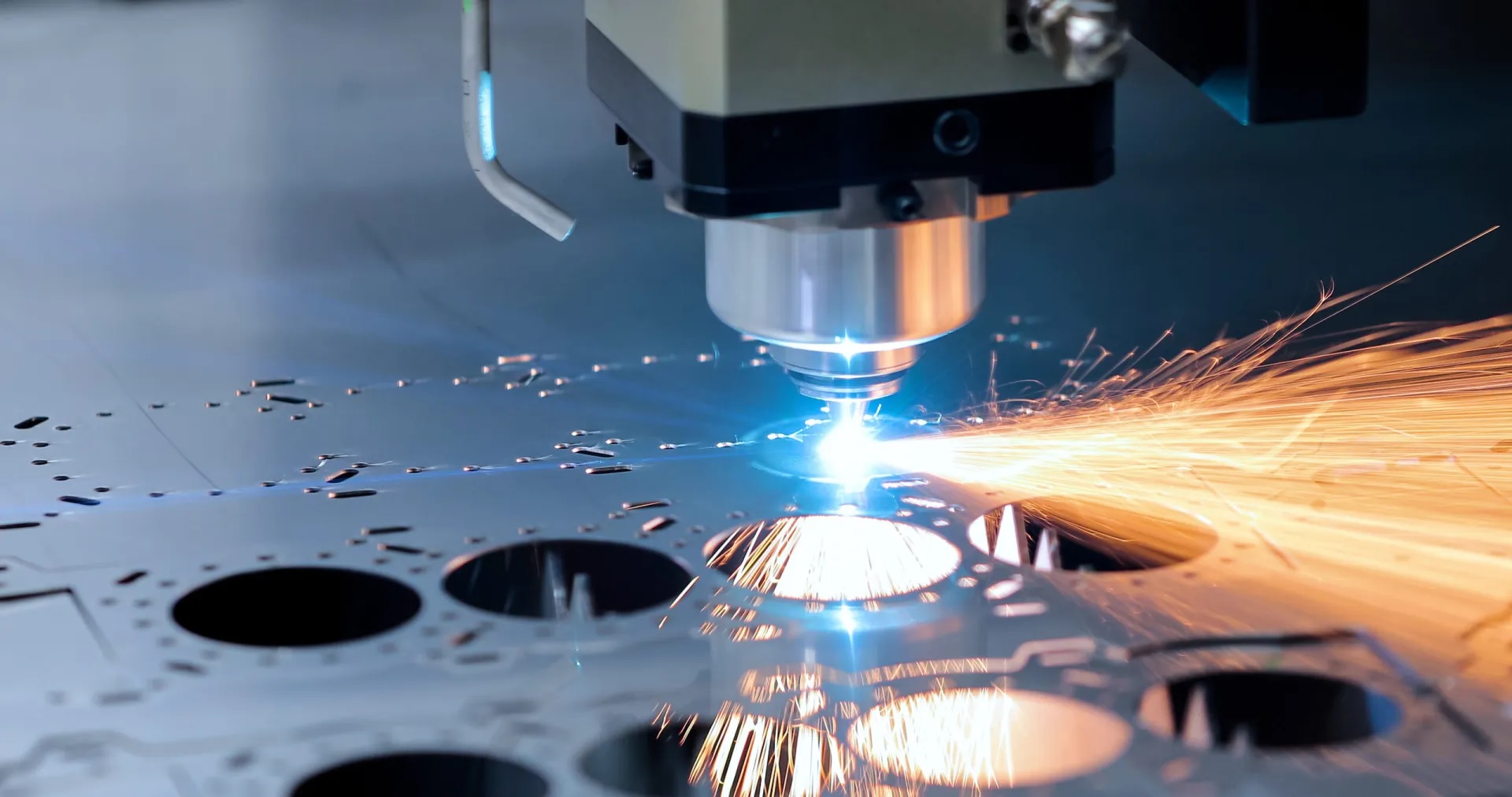

Turret Punching vs Laser Cutting: Choosing the Right Method
Sheet metal fabrication involves cutting, bending, and shaping metal sheets into various parts and products. Some different methods and machines can perform sheet metal cutting, such as turret punching and laser cutting. But which one is better for your project? In this post, we will compare the two techniques and explore their pros and cons.
What is Turret Punching?
Turret punching is a process that uses a punch and a die to create holes and shapes in sheet metal. The punch is a tool that has the desired cutout shape. The die is a metal plate that supports the sheet metal and has a matching hole. The punch presses into the metal with high force, pushing the excess metal into the die and creating the cutout. Turret punching machines have a rotating turret that holds multiple punches and dies of different shapes and sizes. The machine can change the punch and die according to the design and program, allowing for various patterns and configurations. Turret punching machines are CNC controlled, which automates the punching process and ensure accuracy.
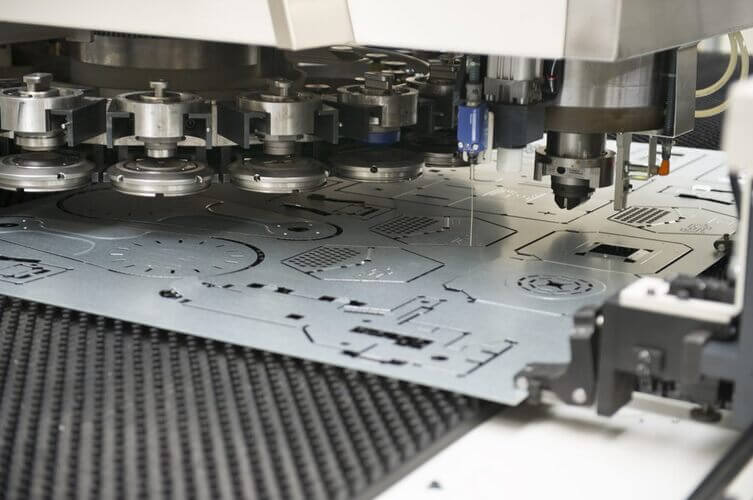

Turret Punching What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a process that uses a focused beam of light and gas to vaporize sheet metal. The laser beam is generated by a laser source and guided by mirrors and lenses to the cutting head. The cutting head focuses the beam into a spot with focussed power density. This heats the sheet metal to its melting and vaporization point. Gas, such as oxygen or nitrogen, blows through the cut area, removing the melted and vaporized metal.
Laser cutting machines are also CNC systems, which control the movement of the cutting head and laser beam. Following the programmed design and material, laser cutting machines can cut complex and intricate shapes and patterns, as well as thick and hard materials.
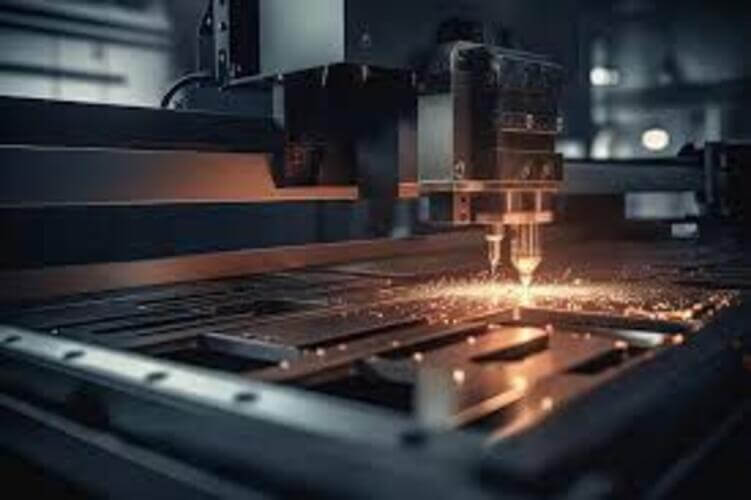

Laser Cutting in Vietnam Advantages and Disadvantages
Laser Cutting
Advantages
- Precision: Laser cutting gives top-notch precision enabling detailed patterns and close measurements. It can create complex forms that other techniques find hard to match.
- Versatility: Like turret punching, laser cutting works on many materials. It stands out because it can slice through thicker stuff – at times up to a few inches deep.
- Minimal Waste: The laser beam is thin, resulting in less material waste compared to traditional cutting methods.
Limitations
- Speed on Thick Materials: While laser cutting is fast, it may be slower than turret punching when working with thicker materials, where cutting speed can decrease significantly.
- Higher Equipment Costs: The initial investment for laser-cutting machinery is generally higher than for turret punching.
- Heat-Affected Zone: The heat from laser cutting can create a heat-affected zone (HAZ), which may require additional finishing processes, particularly in sensitive applications.
Turret Punching
Advantages
- Speed: Turret punching is known for its high speed, particularly for large production runs. Once the tool is set up, it can quickly create multiple identical parts.
- Versatility: The turret punch handles various materials and thicknesses, making it suitable for different uses. It can also do multiple jobs in one go, such as punching, shaping, and notching.
- Cost-Effective for Large Batches: For high-volume production, turret punching can be more economical than laser cutting, as the speed of production offsets the setup time.
Limitations
- Material Constraints: Turret punching is less effective on thicker materials. It generally works best with sheets up to 1/4 inch thick.
- Tooling Costs: The initial cost for tooling and die changes can be significant, especially for custom parts.
- Shape Limitations: Although turret punching is flexible, it has limits when it comes to making complex shapes compared to laser cutting.
Comparing Turret Punching and Laser Cutting
Feature Turret Punching Laser Cutting Accuracy ±0.1mm ±0.01mm Speed Fast for large quantities Fast for complex shapes Material Limitations Limited to metals Can cut various materials Material Thickness Up to 6mm Wide range (thin sheets to thick plates) Tooling Costs High upfront costs Low upfront costs Operating Costs Low operating costs High operating costs Production Cost Cost-effective for large batches Higher for small runs 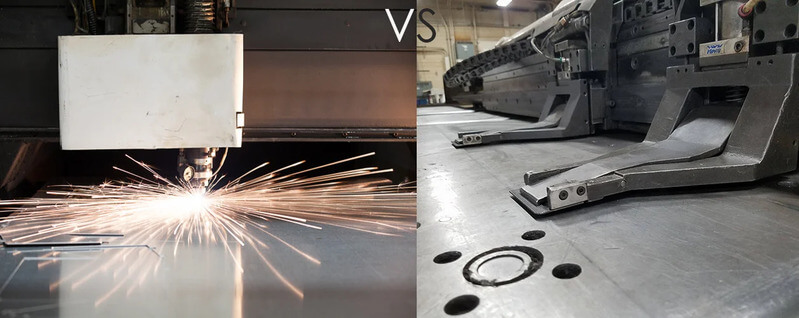
Turret punching vs Laser cutting Applications and Industries
Both methods find applications in various sectors:
- Turret Punching: Common in automotive, electronics, and appliance manufacturing where speed and cost-effectiveness for large batches are crucial.
- Laser Cutting: This shows up in fields like aerospace medical gear, and art where you need exact cuts and tricky shapes.
Making the Right Choice: Turret Punching or Laser Cutting?
To pick between turret punching and laser cutting, you need to think about a few things: how complex the design is, how thick the material is, how much you’re making, and what your budget looks like.
- Turret Punching: Ideal for high-volume production of simpler designs in thinner materials.
- Laser Cutting: Best for low-volume, high-precision work across a range of materials and thicknesses.
Conclusion
Turret punching and laser cutting are both effective methods for cutting and shaping metal, each with its advantages and disadvantages. By considering the factors we talked about here, you can choose the right method for your job. No matter if you go with turret punching or laser cutting, it’s key to team up with a trusted and skilled maker or metal worker to get top-notch results.